Preparation of Ni-W alloy disc for dynamic friction polishing of diamond
-
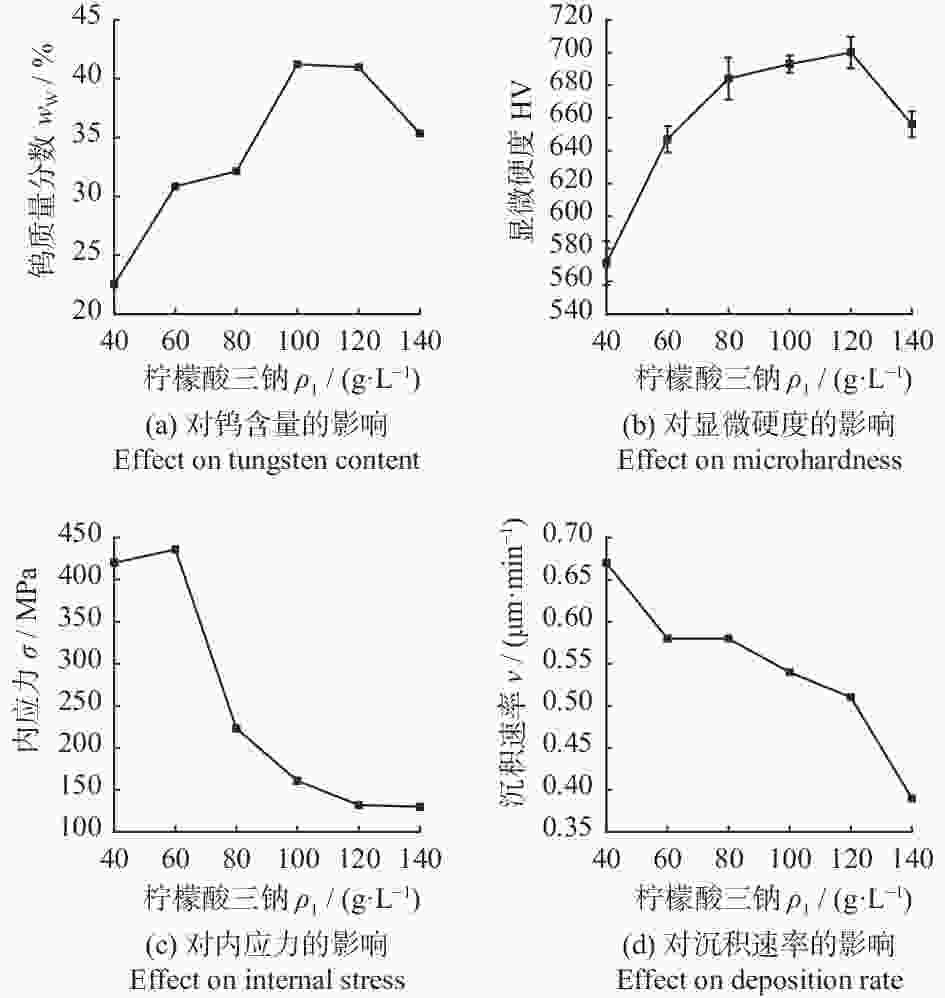
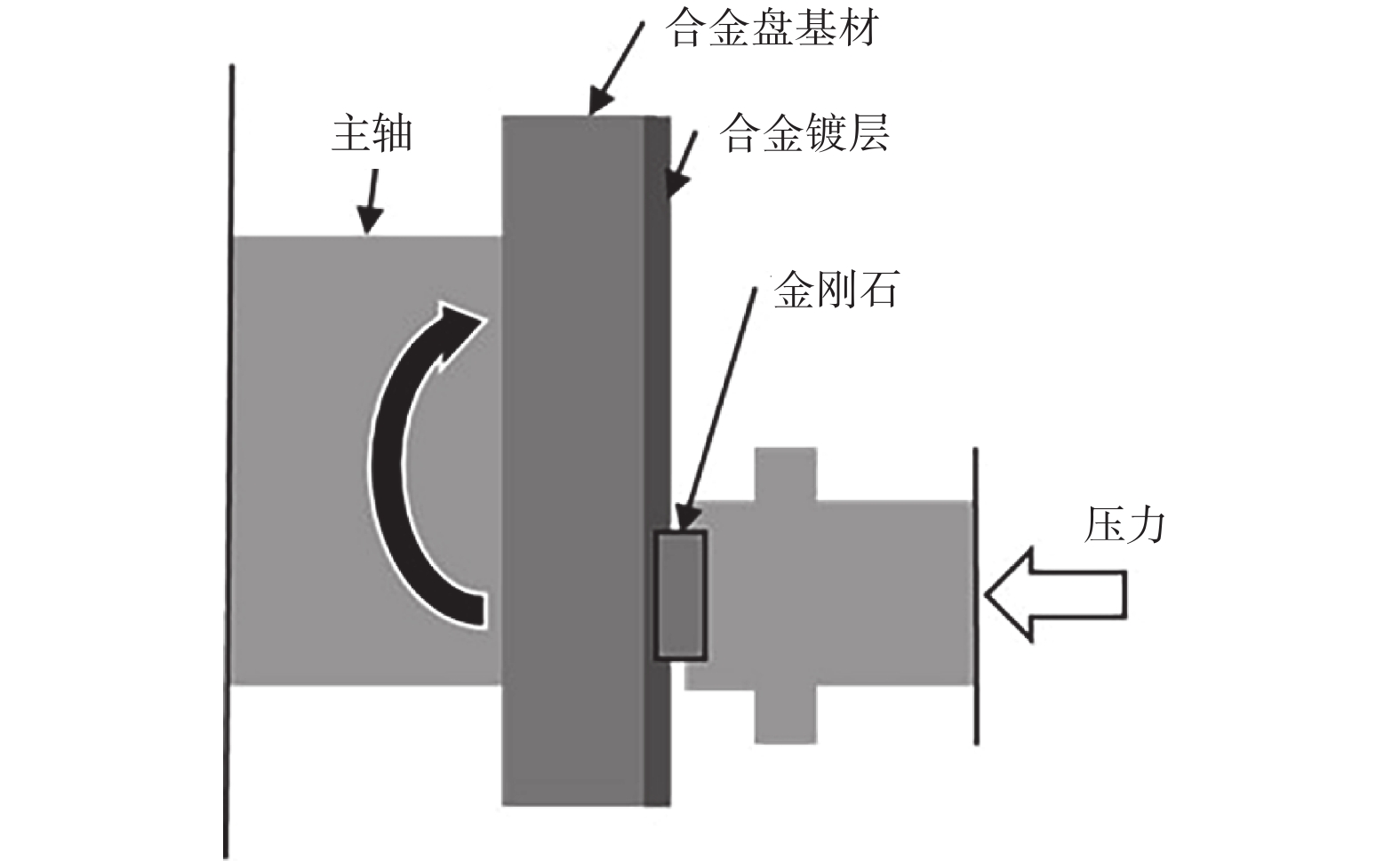
摘要: 为探究镀液成分、工艺条件等因素对Ni-W合金镀层的影响,制备出低内应力、高硬度的Ni-W合金盘,用于金刚石的摩擦化学抛光。采用单一性实验分别探究络合剂浓度、溶液pH、糖精钠浓度对镀层内应力、钨含量、硬度以及沉积速率的影响,并探究不同添加剂对镀层表面整平的效果。最终选用水杨醛为整平剂,并采用反向脉冲电流降低了镀层表面粗糙度,制备出硬度达HV 713,镀层厚度约为0.66 mm的Ni-W合金盘。使用合金盘对金刚石进行摩擦化学抛光,并探究合适的抛光工艺参数。在合金盘转速为8000 r/min,压力为40 N时,金刚石的抛光效果较好,其材料去除率为5.56 μm/min,磨削比达0.394,金刚石表面粗糙度Sa为3.7 nm。使用传统铸铁盘对金刚石进行摩擦化学抛光,通过对比磨损参数发现,Ni-W合金盘能够达到更好的抛光效果。Abstract: To investigate the impact of bath composition and process conditions on Ni-W alloy coating, Ni-W alloy discs with low internal stress and high hardness were prepared for dynamic friction polishing of diamonds. The effects of complexing agent concentration, solution pH, and saccharin sodium concentration on the internal stress, tungsten content, hardness, and deposition rate of the coating were investigated by single experiments. Additionally, the effects of different additives on the surface leveling of the coating were also investigated. Finally, salicylaldehyde was selected as the leveling agent, and the reverse pulse current was applied to reduce the surface roughness of the coating. A Ni-W alloy disc with a hardness of HV 713 and a coating thickness of about 0.66 mm was prepared. Diamond dynamic friction polishing was carried out using these alloy discs to explore appropriate polishing process parameters. The best polishing effects were achieved at a disc speed of 8000 r/min and a pressure of 40 N, yielding a removal rate of 5.56 μm/min, a grinding ratio of 0.394, and a surface roughness (Ra) of 3.7 nm. Comparing wear parameters revealed that Ni-W alloy discs can achieve better polishing effects using traditional cast iron discs in friction chemical polishing of diamonds.
-
Key words:
- diamond /
- Ni-W alloy /
- internal stress of coating /
- tribochemical polishing
-
表 1 初始镀液配方
Table 1. Initial bath formula
成分 化学名称 浓度ρ /(g·L−1) 主盐A 二水合硫酸镍 40.00 主盐B 六水合钨酸钠 40.00 络合剂 柠檬酸三钠 80.00 缓冲剂 硼酸 35.00 导电盐 溴化钠 10.00 表面活性剂 十二烷基硫酸钠 0.15 表 2 实验设备
Table 2. Experimental equipment
设备名称 用途 QUANTA 450扫描电子显微镜 观察Ni-W合金镀层的微观形貌 Oxford X-Max型EDS 测量镀层的元素组分 MVS-1000Z维氏硬度计 测量镀层的显微硬度 VHX-600E超景深显微镜 观察金刚石表面形貌 3D表面光学轮廓Zygo9000 测量金刚石表面粗糙度 DV215CD精密天平 称量镀件质量 XP6梅特勒电子天平 称量金刚石质量 表 3 金刚石的磨削参数对比
Table 3. Comparison of grinding parameters of diamond
参数 铸铁盘 电镀盘 金刚石去除率 Rdia / (μm·min−1) 0.45 5.56 抛光盘磨损率 Rd / (mm³·min−1) 0.45 0.13 磨削比 R2 0.013 0.394 表面粗糙度 Sa / nm 22.8 3.7 -
[1] SUZUKI K, IWAI M, UEMATSU T, et al. Material removal mechanism in dynamic friction polishing of diamond [J]. Key Engineering Materials,2003,460:238-239. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.238-239.235 [2] PAUL E, EVANS C J, MANGAMELLI A, et al. Chemical aspects of tool wear in single point diamond turning [J]. Precision Engineering,1996,18(1):4-19. doi: 10.1016/0141-6359(95)00019-4 [3] JONHNSON O. Catalysis and the interstitial-electron model for metals [J]. Journal of Catalysis. 1973, 1(21): 1-54. [4] 马兴伟. 高速摩擦抛光金刚石膜用FeAl基合金抛光盘的制备及性能研究 [D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2011.MA Xingwei. Study on the fabracation and properties of FeAl based alloy polishing plate for dynamic friction polishing of diamond film [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2011. [5] 孔军. 高速摩擦抛光金刚石用抛光盘的研制[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2013.KONG Jun. Develop of polishing plate used in dynamic friction polishing of diamond. [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2013. [6] 林佳志. 摩擦化学抛光单晶金刚石的工艺研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2015.LIN Jiazhi. Research on dynamic friction polishing technology for single crystal diamond [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2015. [7] 史双佶. 金刚石摩擦化学抛光用抛光盘制备及抛光机理研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2016.SHI Shuangji. Preparation and polishing mechanism research of polishing plate used for dynamic friction polishing diamond [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2016. [8] KAMPMANN A, SITTINGER V, RECHID J, et al. Large area electrodeposition of Cu(In, Ga)Se2 [J]. Thin Solid Films,2000,361-362:309-313. doi: 10.1016/S0040-6090(99)00863-9 [9] HUANG C H, SHE W Y, WU H M. Study of stress reducers in nickel-tungsten electroforming baths [J]. Plating and Surface Finishing,1999,86(12):79-83. [10] MIZUSHIMA I, TANG P T, HANSEN H N, et al. Residual stress in Ni-W electrodeposits [J]. Electrochimica Acta,2006,51(27):6128-6134. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2005.11.053 [11] LIU R, WANG H, LI X P, et al. Study of internal stress of amorphous Ni-W alloy films [J]. Materials Science and Technology,2009,25(8):960-968. doi: 10.1179/174328408X311071 [12] BERKH O, BURSTEIN L, SHACHAM-DIAMAND Y, et al. The chemical and electrochemical activity of citrate on Pt electrodes [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society,2011,158(6):F85. doi: 10.1149/1.3560572 [13] 李延伟, 尚雄, 姚金环, 等. 糖精对柠檬酸盐中性电镀镍影响的研究 [J]. 电镀与精饰,2013,35(9):43-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3849.2013.09.011LI Yanwei, SHANG Xiong, YAO Jinhuan, et al. Investigations on influences of saccharin additive on nickel electroplating in neutral citrate electrolyte [J]. Plating & Finishing,2013,35(9):43-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3849.2013.09.011 [14] 成旦红, 郭鹤桐, 刘淑兰. 金属沉积层的应力起源及影响因素 [J]. 电镀与精饰,1992(6):15-19.CHENG Danhong, GUO Hetong, LIU Shulan. Stress origin and influence factors of metal deposits [J]. Plating & Finishing,1992(6):15-19. [15] MOCKUTE D, BERNOTIENE G. The interaction of additives with the cathode in a mixture of saccharin, 2-butyne-1, 4-diol and phthalimide during nickel electrodeposition in a Watts-type electrolyte [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology,2000,135(1):42-47. doi: 10.1016/S0257-8972(00)00862-8 [16] 冯立明, 电镀工艺学 [M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2010.FENG Liming, et al. Electroplating technology [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2010. [17] 安茂忠. 电镀理论与技术 [M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2004.AN Maozhong. Electroplating theory and technology [M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2004. [18] BRENNER A. Electrodeposition of tungsten alloys containing cobalt, nickel, and/or iron [M]// BRENNER A. Electrodeposition of Alloys. New York: Academic Press, 1963: 347-412. [19] 李延伟, 黄晓曦, 杨哲龙, 等. 镀镍层内应力及其测量方法 [J]. 电镀与环保,2011,31(1):4-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4742.2011.01.002LI Yanei, HUANG Xiaoxi, YANG Zhelong, et al. Internal stress of nickel coating and its measuring methods [J]. Electroplating& Pollution Control,2011,31(1):4-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4742.2011.01.002 [20] BRATOEVA M, ATANASOV N. Effect of sulfamate-citrate electrolyte pH on the Ni-W alloy electrodeposition [J]. Russian Journal of Electrochemistry,2000,36(1):60-63. doi: 10.1007/BF02757797 [21] OBRADOVIĆ M D, STEVANOVIĆ R M, DESPIĆ A R. Electrochemical deposition of Ni–W alloys from ammonia–citrate electrolyte [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry,2003,552:185-196. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0728(03)00151-7 [22] LI Y, YAO J, HUANG X. Effect of saccharin on the process and properties of nickel electrodeposition from sulfate electrolyte [J]. International Journal of Metallurgical & Materials Engineering,2016,2:149450140. doi: 10.15344/2455-2372/2016/123 [23] SHREERAM D D, LI S, BEDEKAR V, et al. Effect of reverse pulse time on electrodeposited Ni-W coatings [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology,2017,325:386-396. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.06.037 [24] 彭超, 殷志伟, 汪晓, 等. 十二烷基硫酸钠和1,4-丁炔二醇电沉积Ni-W合金的机理 [J]. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程,2011,16(2):167-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2011.02.003PENG Chao, YIN Zhiwei, WANG Xiao, et al. Mechanism of sodium lauryl sulfate and 1,4-butynediol in electrodepositing Ni-W alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering of Powder MetaIlurgy,2011,16(2):167-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2011.02.003 [25] KUMAR U P, KENNADY C J. Influence of vanillin on the corrosion behavior of Ni-W alloy electrodeposits and its properties [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry,2016,782:67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.10.009 [26] KUMAR U P, KENNADY C J, ZHOU Q. Effect of salicylaldehyde on microstructure and corrosion resistance of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni-W alloy coatings [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology,2015,283:148-155. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2015.10.056 -




 下载:
下载:













 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
