Evolution behavior of microstructure and properties of Cu-20Sn-15Ti filler metal regulated by Si
-
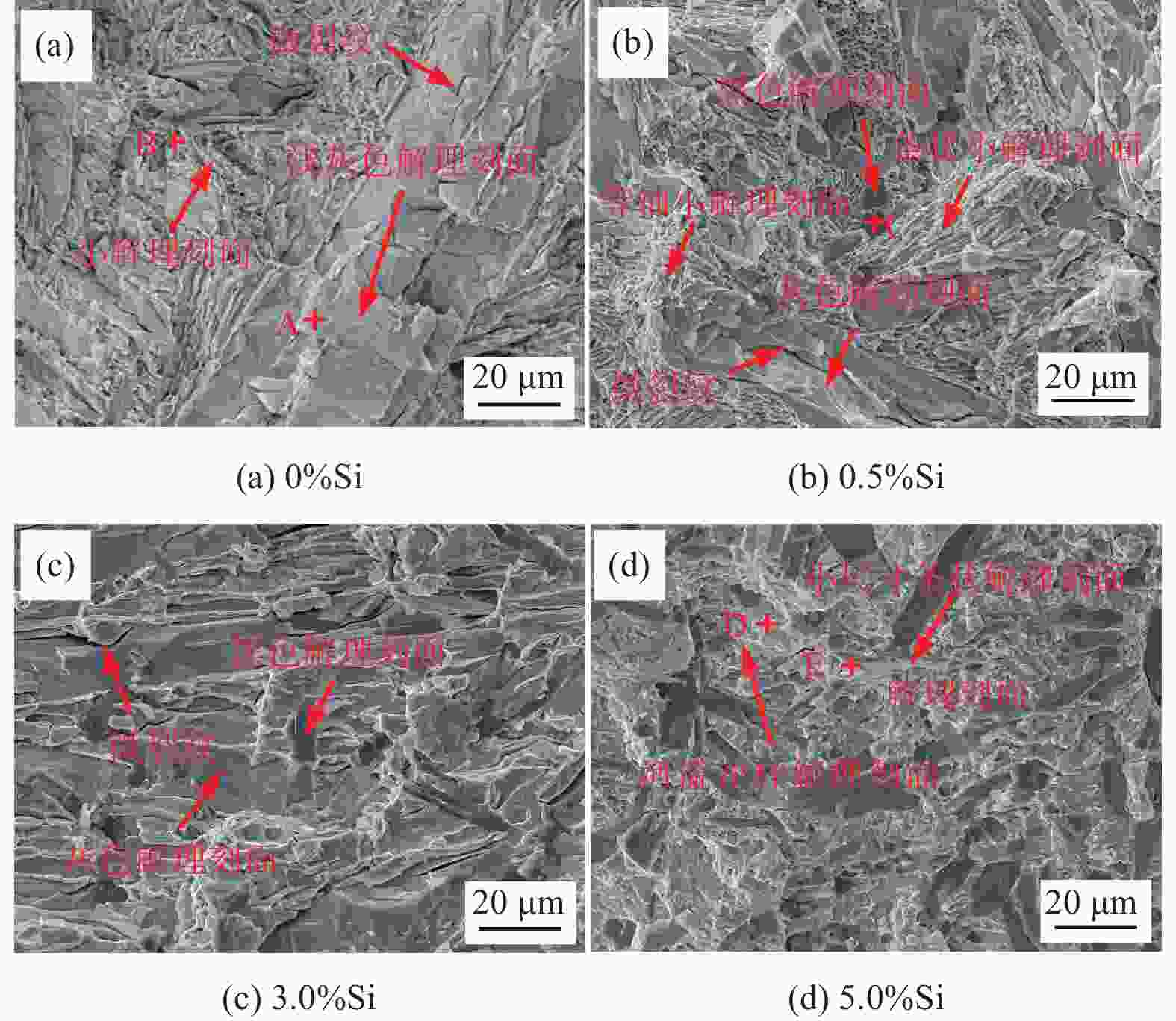
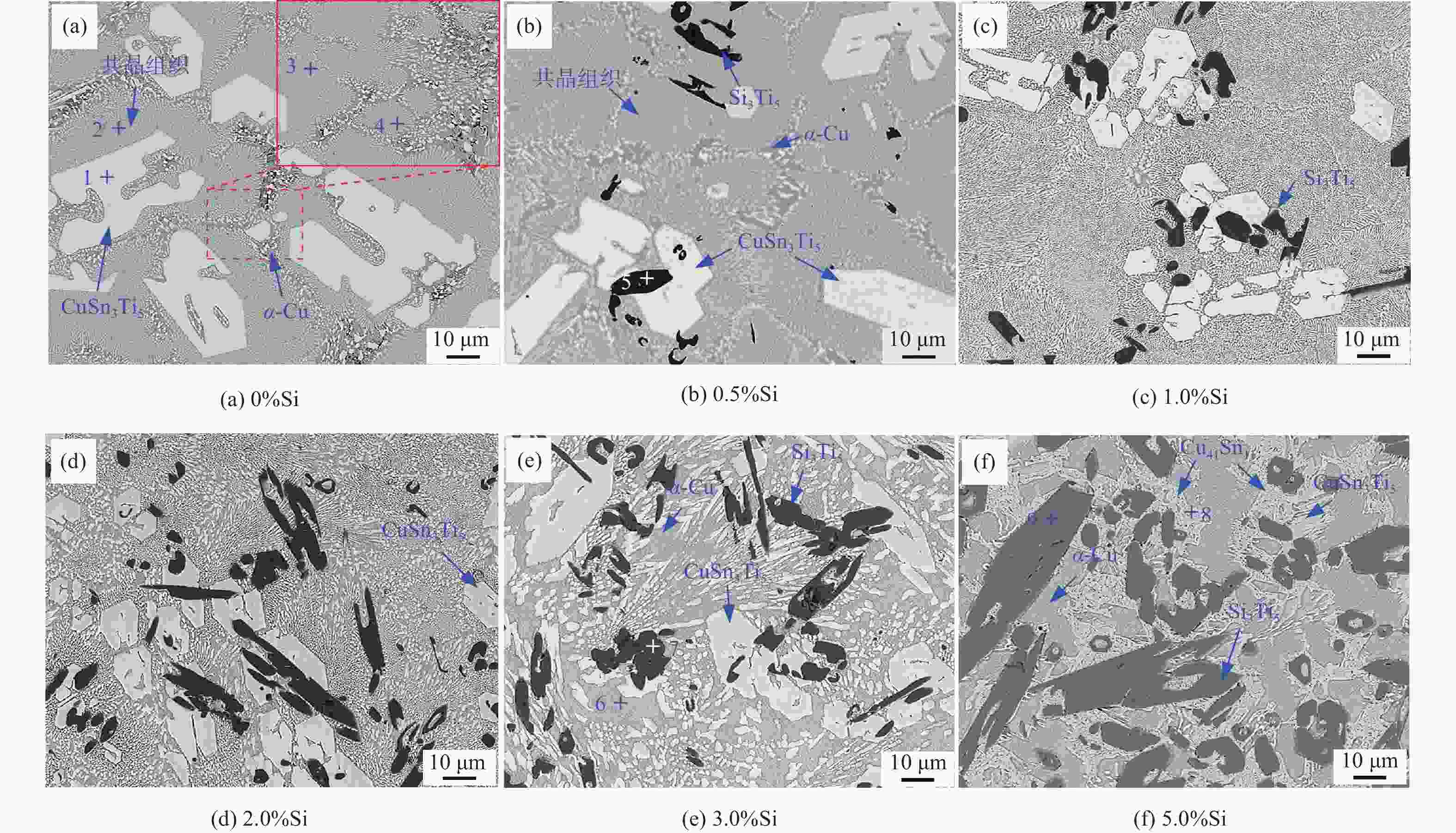
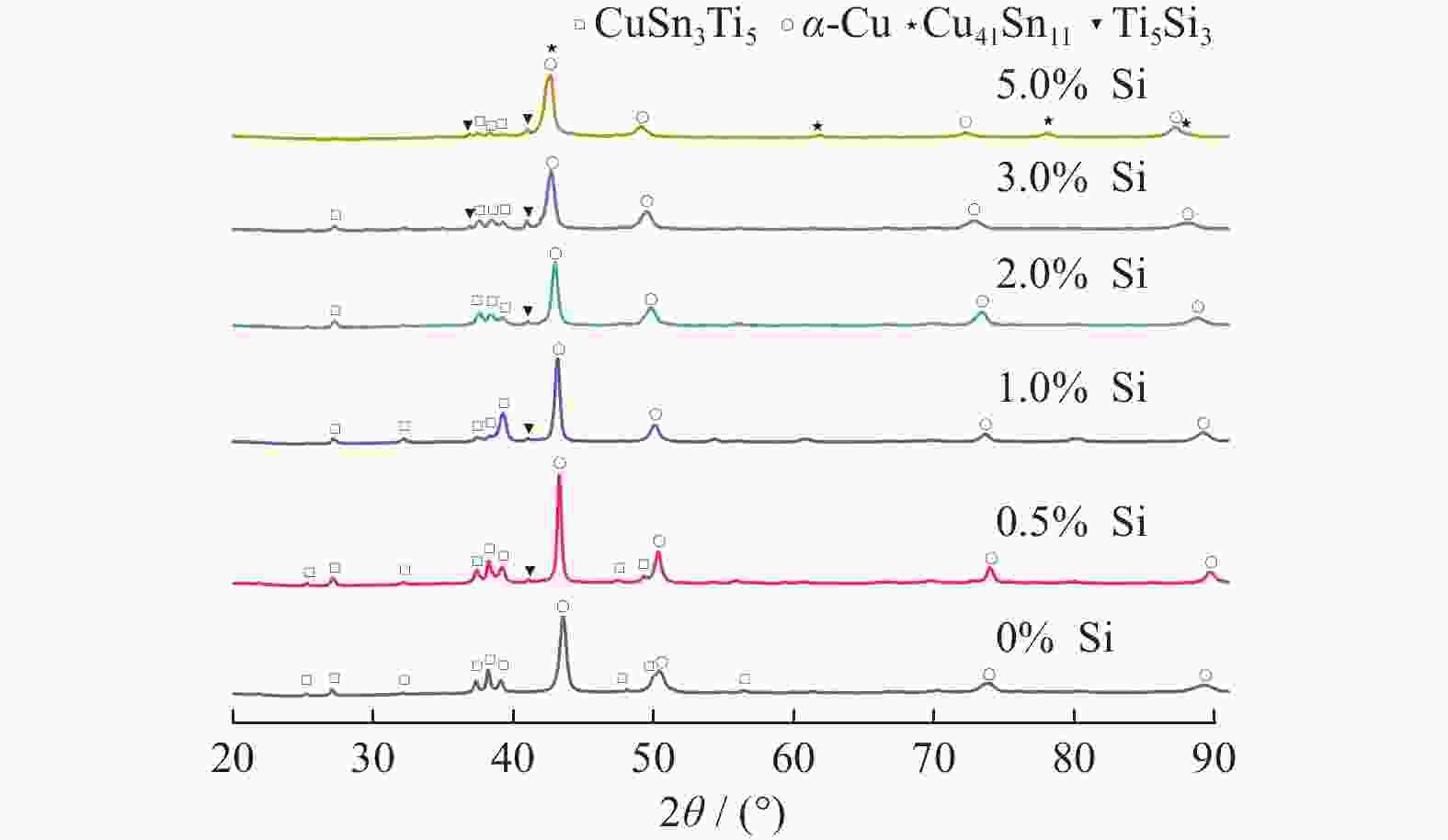
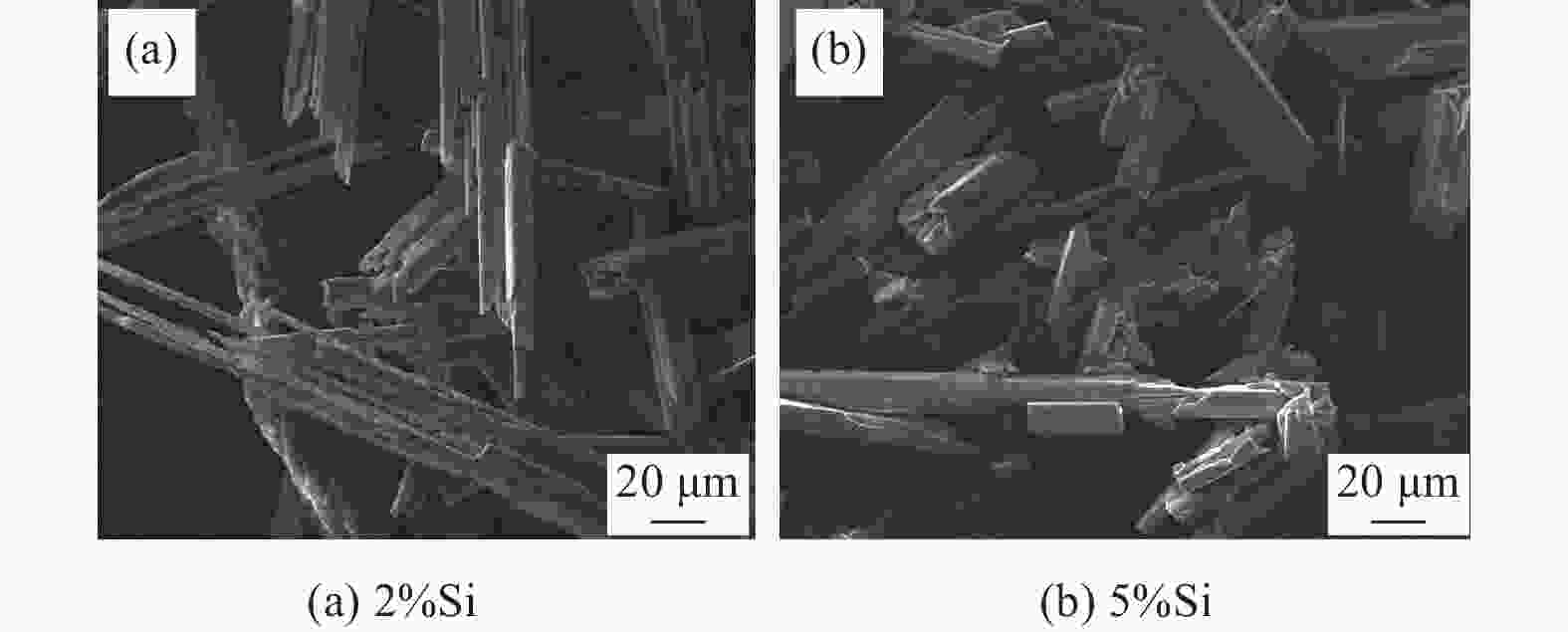
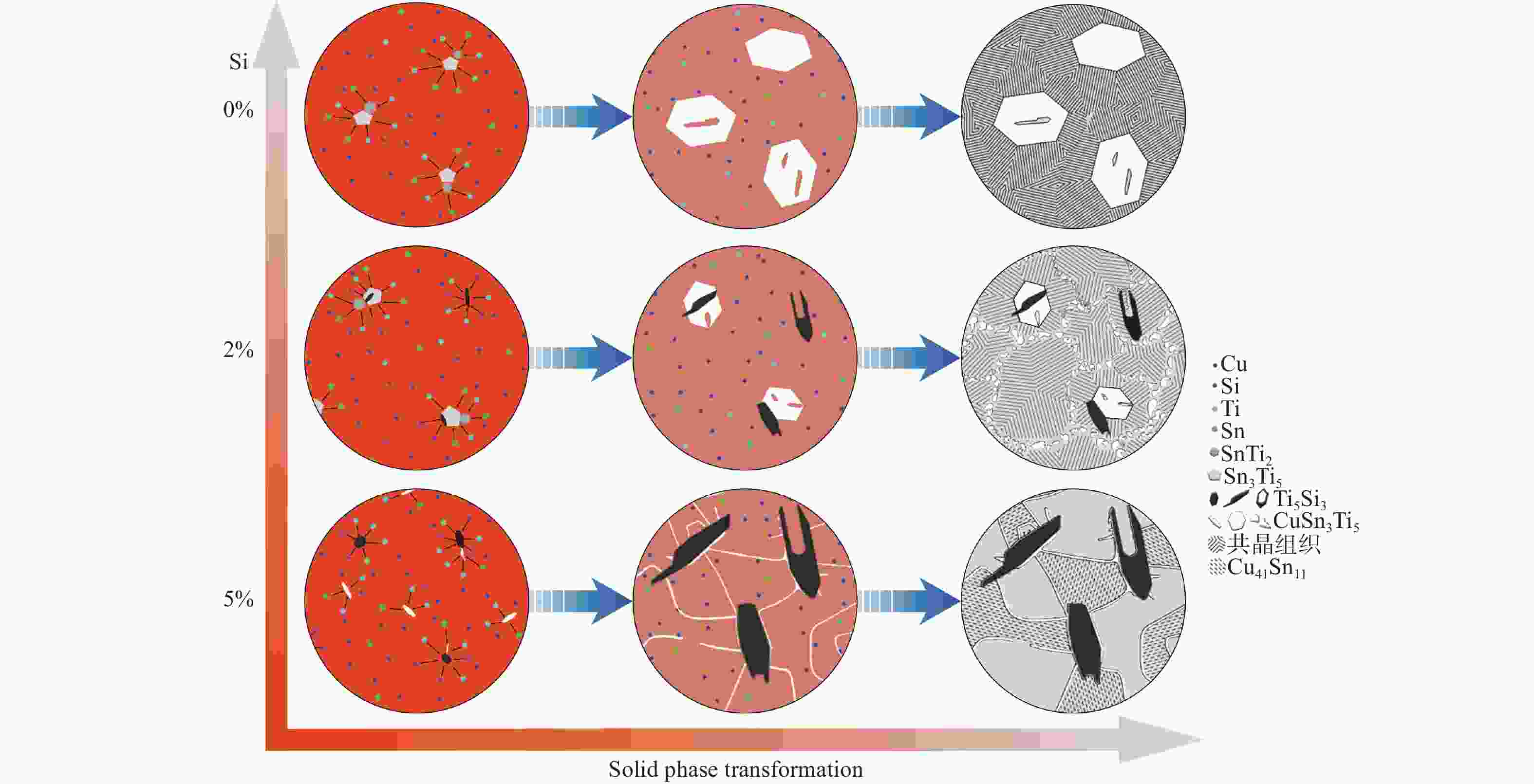
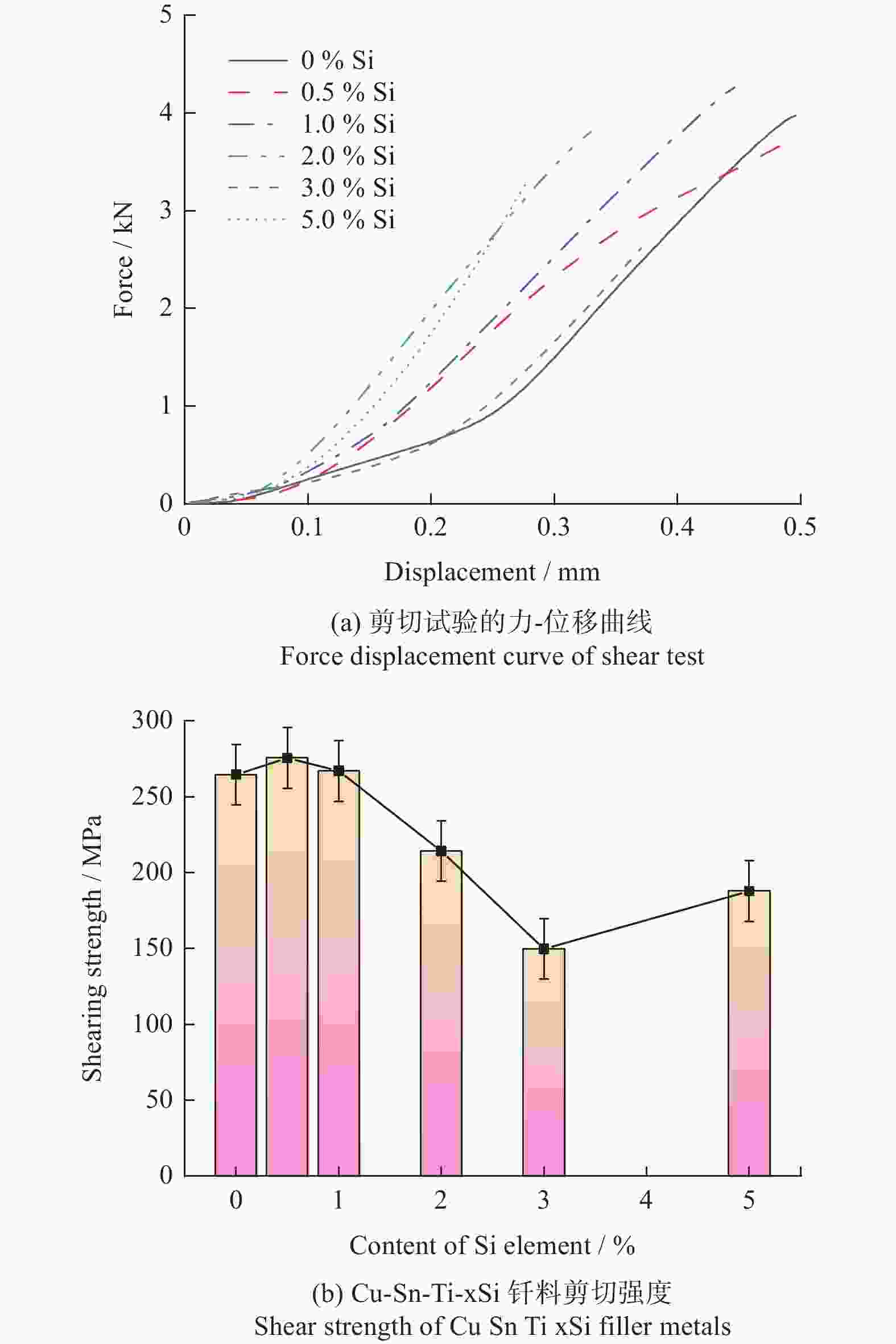
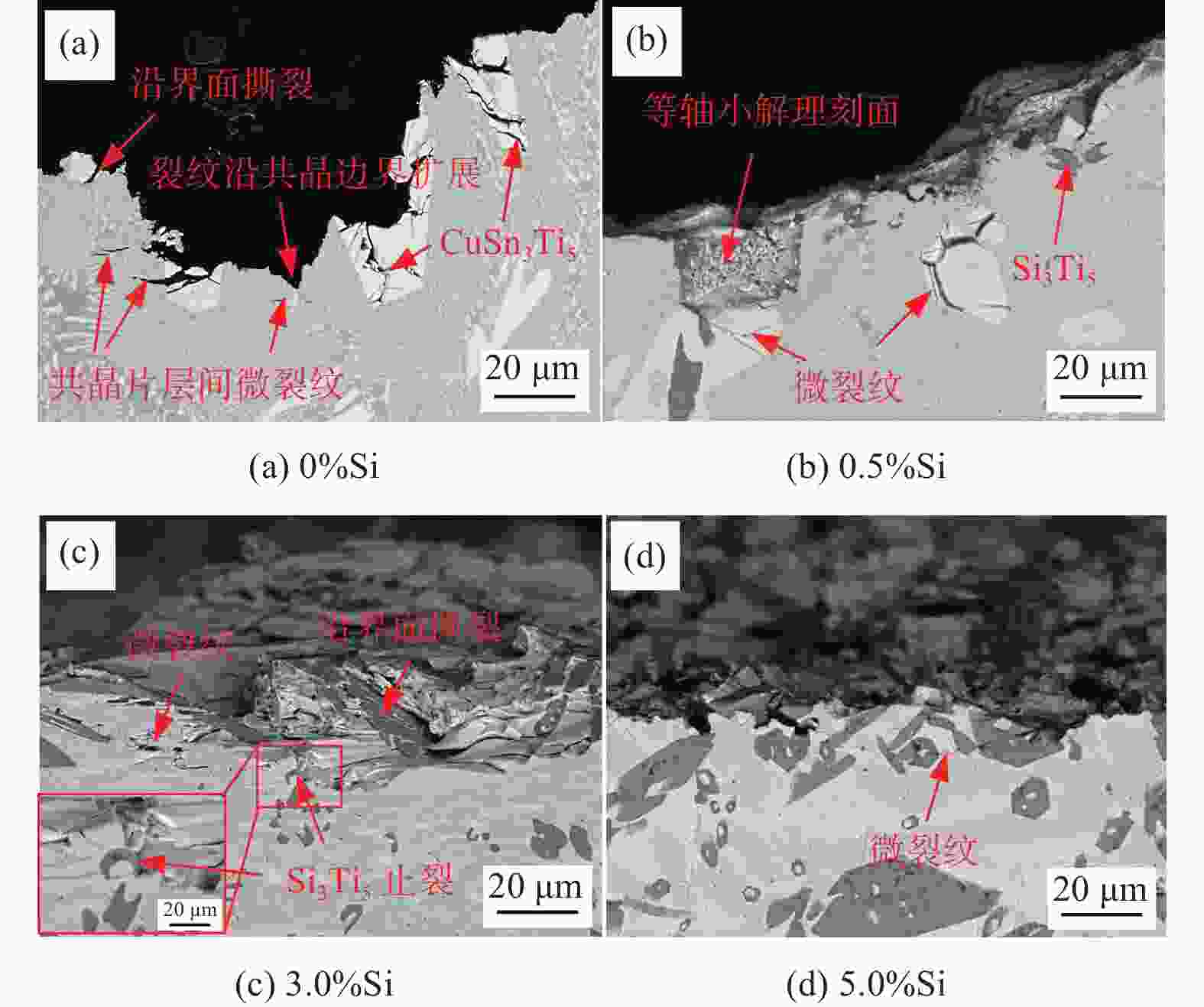
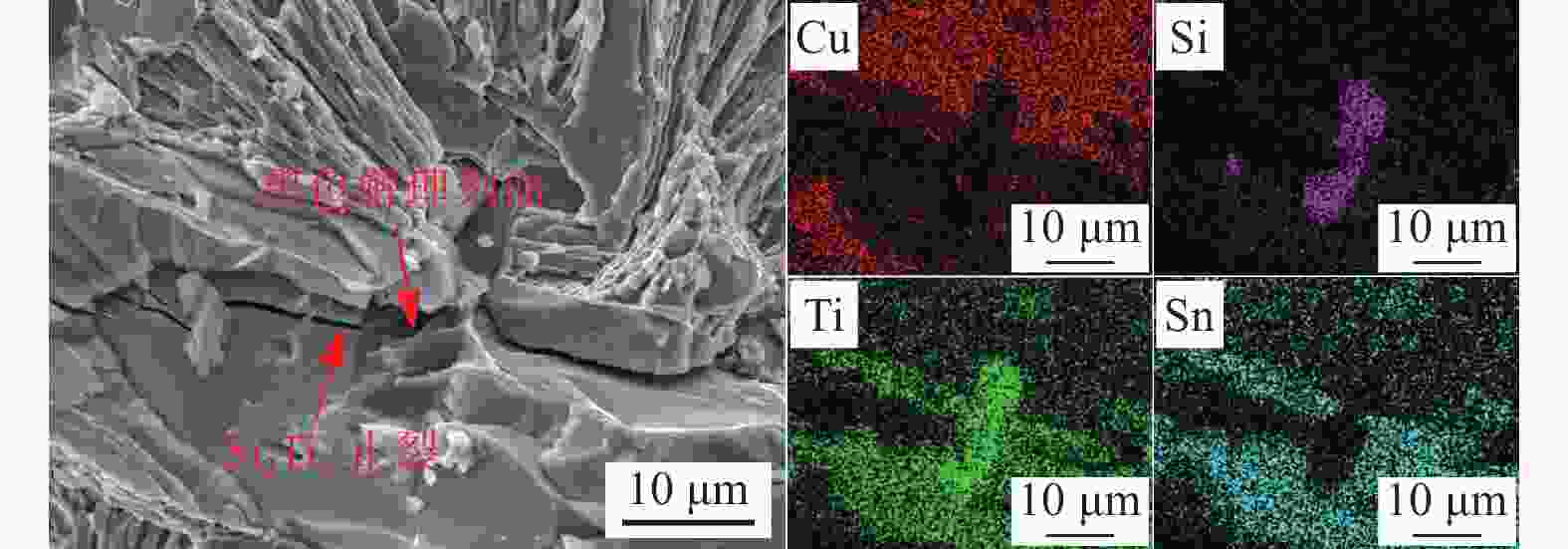
摘要: 为通过成分调控改善Cu-Sn-Ti钎料的显微组织及性能,采用扫描电子显微镜、X射线衍射仪及EDS能谱分析等设备,研究了Si对Cu-20Sn-15Ti钎料显微组织与性能的影响规律。结果表明:Cu-20Sn-15Ti钎料的显微组织为大尺寸多边形状CuSn3Ti5相、共晶组织和α-Cu相。添加少量的Si(质量分数≤2.0%)可细化钎料中多边形状CuSn3Ti5相,并生成小尺寸Si3Ti5相,较多的Si(质量分数≥3.0%)会造成多边形状CuSn3Ti5相分化离散、共晶组织粗化减少,Si3Ti5相含量增加且粗化,当Si含量增至5.0%时,钎料不再生成多边形状CuSn3Ti5相和共晶组织,Ti主要用于生成Ti5Si3相,显微组织主要为Ti5Si3相、α-Cu相、Cu41Sn11相和少量条状CuSn3Ti5相;与Cu、Sn相比,Si与Ti具有更强的化学亲和力,Si优先与Ti反应生成Ti5Si3相;Ti5Si3相的三维组织形貌为棱柱状,且呈团聚附生特征,粗条状Ti5Si3相具有中心或侧面孔洞缺陷,孔洞的形成主要与其生长机制有关;随着Si含量的增加,钎料的剪切强度呈“升高-降低-升高”的趋势,断口形貌由准解理断裂和解理断裂的混合形态向解理断裂转变;CuSn3Ti5相易破碎开裂成为起裂源,不同粗大状态CuSn3Ti5相的存在均在一定程度上恶化钎料剪切强度。
-
关键词:
- Cu-Sn-Ti钎料 /
- 金刚石 /
- 显微组织 /
- CuSn3Ti5相
Abstract: To improve the microstructure and properties of Cu-Sn-Ti brazing alloy through component control, the effect of Si on the microstructure and properties of Cu-20Sn-15Ti brazing filler metals was studied using scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and EDS energy spectrum analysis. The results show that the microstructure of Cu-20Sn-15Ti brazing filler metal is composed of large-sized polygonal CuSn3Ti5 phase, eutectic structure and α-Cu phase. A small amount of Si (≤ 2.0wt%) refines the polygonal-shaped CuSn3Ti5 phase in the brazing filler metal and generates small-sized Si3Ti5 phase. In contrast, a larger amount of Si (≥ 3.0wt%) differentiates the polygonal-shape CuSn3Ti5 phase, reduces the proportion of eutectic structure, and increases the content and size of the Si3Ti5 phase. When the Si content increases to 5.0wt%, the filler metal no longer generates polygonal-shaped CuSn3Ti5 phase and eutectic structure. Instead, Ti primarily forms Ti5Si3 phase, and the microstructure mainly consists of Ti5Si3 phase, α- Cu phase, Cu41Sn11 phase, and a small amount of strip-shaped CuSn3Ti5 phase. Compared with Cu and Sn, Si has a stronger chemical affinity with Ti and preferentially reacts with Ti to form Ti5Si3 phase. The three-dimensional structure of Ti5Si3 phase is prismatic and exhibits agglomerated growth characteristics. The coarse strip Ti5Si3 phase has central or lateral pore defects, which are mainly related to the growth mechanism. As the Si content increases, the shear strength of the filler metals shows a trend of “increasing-decreasing-increasing”, and the fracture morphology transitions from a mixed morphology of quasi-cleavage fracture and cleavage fracture to cleavage fracture. The CuSn3Ti5 phase is prone to breakage and cracking, becoming the source of cracking. The presence of coarse CuSn3Ti5 phase in different states can deteriorate the shear strength of the brazing filler metals to some extent.-
Key words:
- Cu-Sn-Ti filler metal /
- diamond /
- microstructure /
- CuSn3Ti5 phase
-
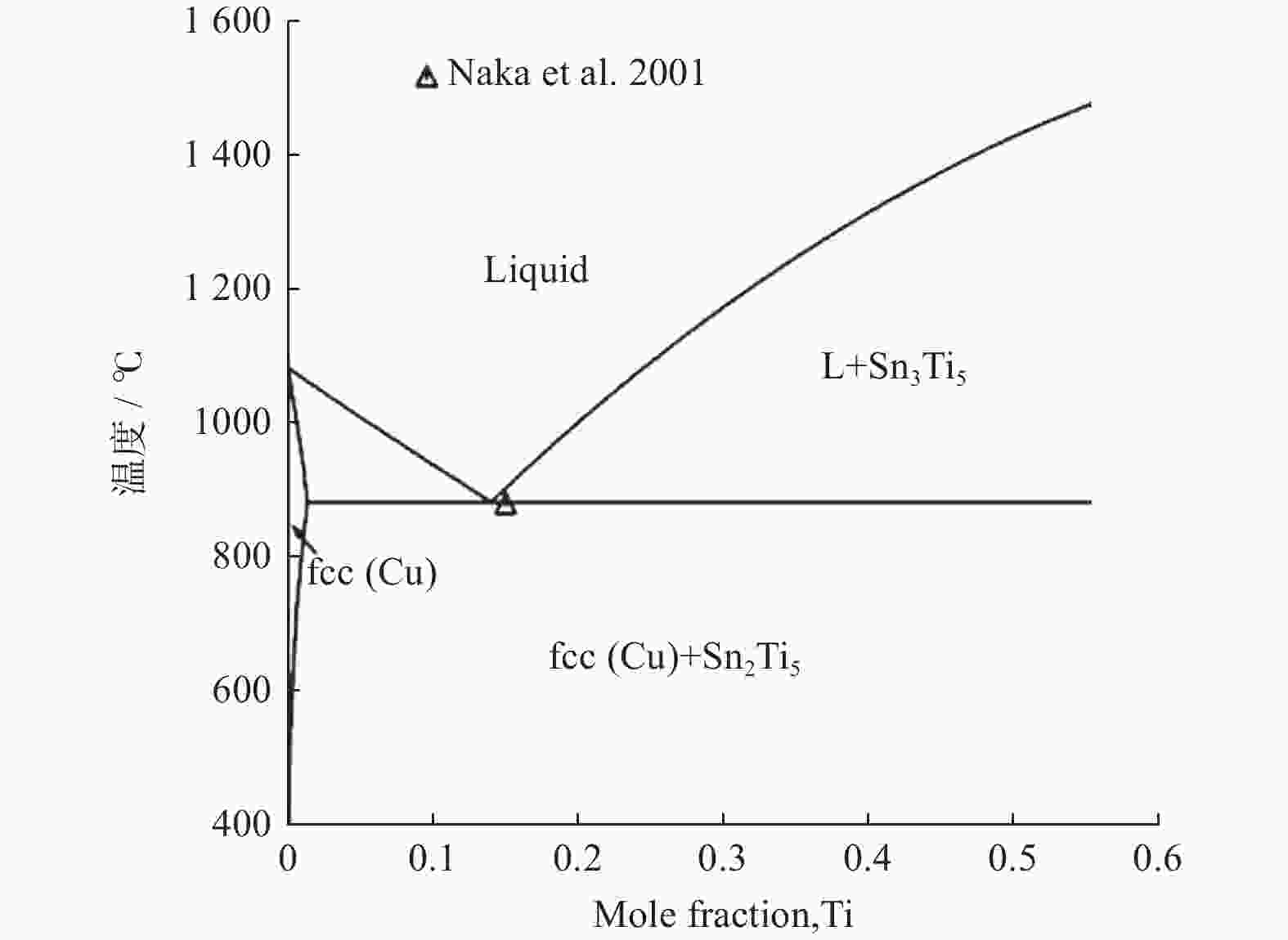
图 7 Cu-CuSn3Ti5计算等值线截面[20]
Figure 7. The calculated isopleth section of Cu-CuSn3Ti5
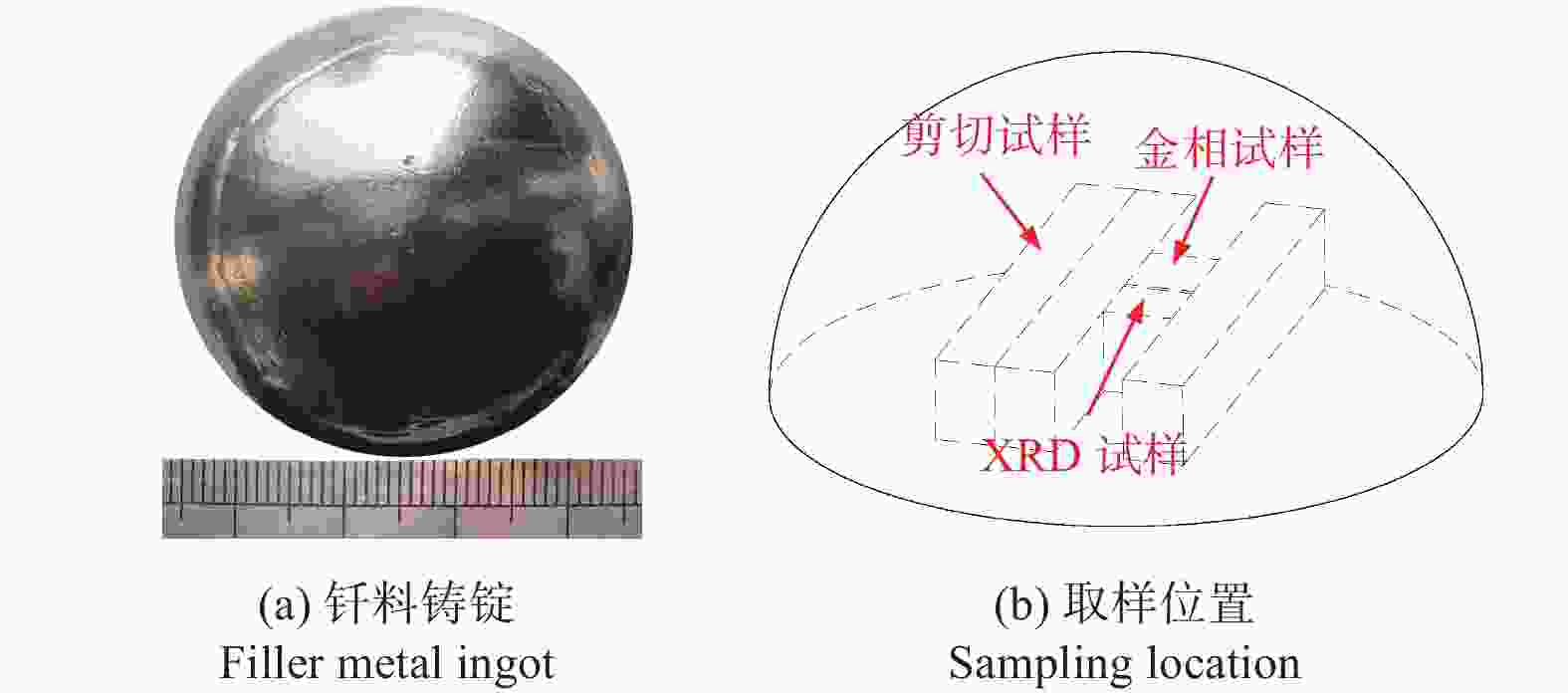
表 1 Cu-20Sn-15Ti-xSi钎料含义成分
Table 1. Composition of Cu-20Sn-15Ti-xSi filler metal
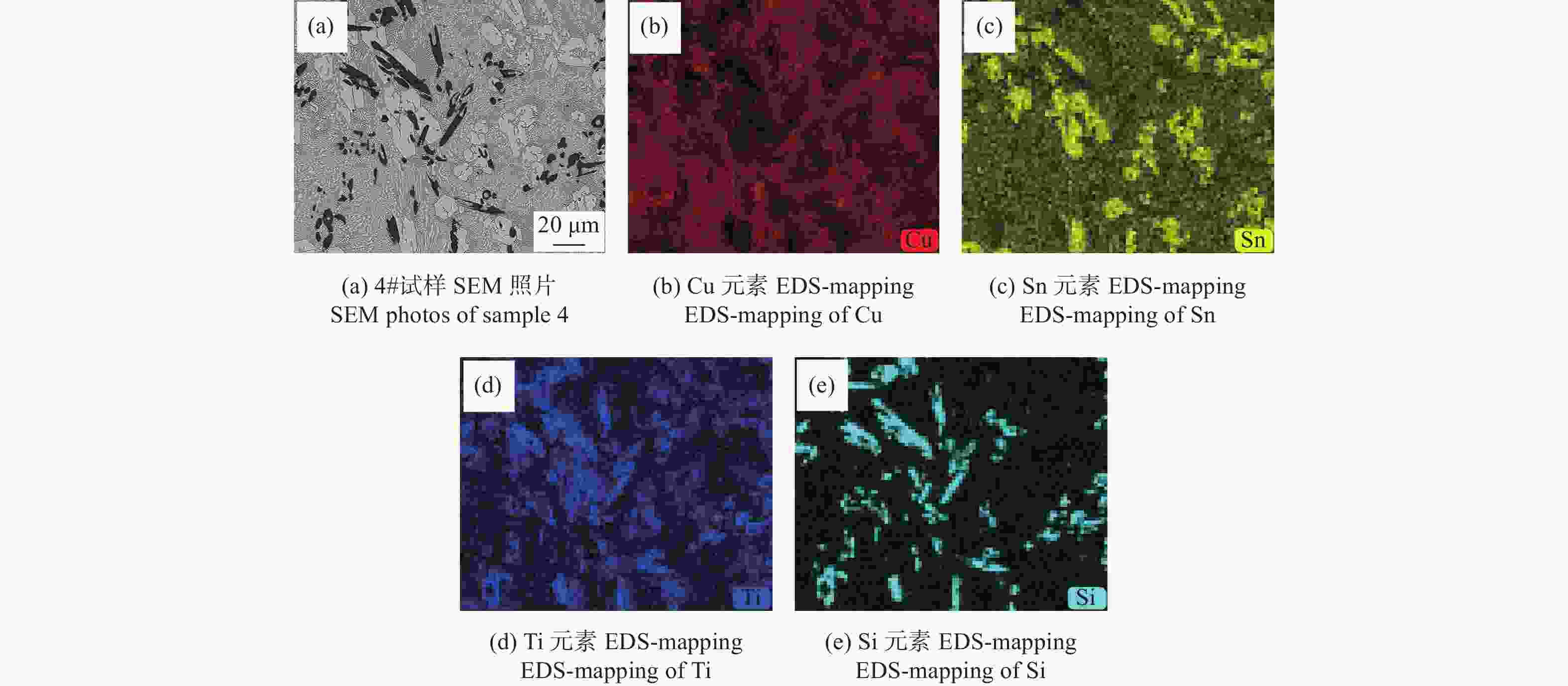
序号 ωCu/% ωSn/% ωTi/% ωSi/% 1# 65.00 20.00 15.00 - 2# 64.51 19.99 15.00 0.50 3# 64.04 19.98 14.98 1.00 4# 63.01 20.00 14.99 2.00 5# 61.98 20.00 15.02 3.00 6# 59.99 20.00 15.01 5.00 表 2 图2中各点能谱分析结果(at%)
Table 2. EDS analysis results of each point in Fig.2(at%)
测试点 Cu Sn Ti Si 平衡相 1 13.41 34.43 52.17 - CuSn3Ti5 2 76.71 8.42 14.88 - 共晶组织 3 17.53 32.64 49.83 - CuSn3Ti5 4 96.29 1.06 2.65 - α-Cu(富Ti) 5 2.00 0.73 61.12 36.15 Si3Ti5 6 90.79 6.94 1.34 0.93 α-Cu(富Sn) 7 1.43 0.53 60.84 37.20 Si3Ti5 8 77.69 20.60 0.50 1.20 Cu41Sn11 9 1.87 0.64 60.27 37.23 Si3Ti5 表 3 合金元素系统参数
Table 3. Parameters of alloy element systems
合金系统 (Z/rk)A/(Z/rk)B 电负性差△x 化学亲和力参数η Cu-Ti 0.176 0.4 0.576 Sn-Ti 0.956 0.3 1.256 Si-Ti 1.656 0.3 1.956 表 4 图9中各点能谱分析结果(at%)
Table 4. EDS analysis results of each point in Fig.9(at%)
测试点 Cu Sn Ti Si 平衡相 A 13.99 33.25 52.76 - CuSn3Ti5 B 76.98 8.33 14.69 - 共晶组织 C 6.84 1.91 52.58 38.68 Si3Ti5 D 69.46 22.13 6.86 1.55 Cu41Sn11 E 12.51 31.12 50.41 5.96 CuSn3Ti5 -
[1] 毛雅梅, 黑鸿君, 高洁, 等. 钎焊金刚石研究进展及其工具的应用 [J]. 机械工程学报,2022,58(4):80-93. doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.04.080MAO Yamei, HEI Hongjun, GAO Jie, et al. Research progress of brazed diamond and its tool application [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2022,58(4):80-93. doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.04.080 [2] 曹忠溪, 周玉梅, 张凤林, 等. 钎焊金刚石耐磨涂层制备及其磨损性能[J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程, 2019, 39(3): 93-101.CAO Zhongxi, ZHOU Yumei, ZHANG Fenglin, et al. Preparation and wear performance of brazed diamond wear-resistant coating[J]. Diamond &. Abrasives Engineering, 2019, 39(3): 93-101. [3] WANG S Y, XIAO B, XIAO H Z, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the diamond/1045 steel joint brazed using Ni-Cr + Mo composite filler [J]. Diamond & Related Materials,2023,133:109691. [4] ZHANG L. Filler metals, brazing processing and reliability for diamond tools brazing: A review [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2021,66:651-668. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.04.015 [5] 戴秋莲, 徐西鹏, 王永初. 金属结合剂对金刚石把持力的增强措施及增强机制评述 [J]. 材料科学与工程,2002,20(3):465-468.DAI Qiulian, XU Xipeng, WANG Yongchu. Review on measures and mechanisms for enhancing the holding force of diamond by metal binders [J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering,2002,20(3):465-468. [6] 王树义, 肖冰, 肖皓中, 等. 镍基钎料真空钎焊镀钨金刚石的研究[J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程, 2023, 43(2): 202-209.Dai Q L, Xu X P, Wang Y C. Measures used to improve bonding of diamond to matrix and bonding mechanisms[J]. Materials Science & Engineering, 2002, 20(3): 465-468. [7] 杨沁, 凌景亮, 崔长彩, 等. 高频感应钎焊金刚石磨粒剪切失效的试验研究[J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程, 2019, 39(5): 85-91.YANG Qin, LING Jingliang, CUI Changcai, et al. Experimental study on shear failure of diamond abrasive particles in high-frequency induction brazing[J]. Diamond &. Abrasives Engineering, 2019, 39(5): 85-91. [8] 龙伟民, 郝庆乐, 傅玉灿, 等. 金刚石工具钎焊用连接材料研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(23): 23138-23144.LONG Weimin, HAO Qingle, FU Yucan, et al. Research progress of connection materials for brazing diamond tools[J]. Materials Review, 2020, 34(23): 23138-23144. [9] 卢金斌, 贺亚勋, 张旺玺. 等. CuSnTiNi钎料真空钎焊金刚石 [J]. 焊接学报,2017,38(6):125-128.LU Jinbin, HE Yaxun, ZHANG Wangxi, et al. Analysis on vacuum brazing diamond using CuSnTiNi [J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution,2017,38(6):125-128. [10] 高先哲, 肖冰, 管海军, 等. Cu-Sn-Ti钎料的改性设计及性能分析[J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程, 2018, 38(1): 32-36.GAO Xianzhe, XIAO Bing, GUAN Haijun, et al. Modification design and performance analysis of Cu-Sn-Ti solder[J]. Diamond &. Abrasives Engineering, 2018, 38(1): 32-36. [11] CUI B, ZHAO W X, ZUO R Z, et al. Effect of rare earth alloy addition on the microstructure and abrasion resistance of brazed diamonds with Cu-Sn-Ti filler metal[J]. Diamond & Related Materials, 2022, 126: 109110 [12] LI H L, CHEN J, CUI B, et al. Effects of Ga on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Cu-Sn-Ti Filler [J]. Advanced Science News,2022,219(2):2100203. [13] CUI B, YAN P P, ZHAO W X, et al. Influence of Ge content on the interfacial characteristics and wear resistance of brazed synthetic diamond grains of Cu-based composite filler [J]. Welding in the World,2022,66(10):1975-1987. doi: 10.1007/s40194-022-01328-y [14] CUI B, LIU Z W, ZUO R Z, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of vacuum brazed diamond abrasive segments with zirconium carbide reinforced Cu-based active filler metals [J]. Diamond & Related Materials,2022,126:109091. [15] CUI B, ZHAO W X, ZUO R Z, et al. The abrasion resistance of brazed diamond using Cu-Sn-Ti composite alloys reinforced with boron carbide [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2022,124:108926. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2022.108926 [16] DUAN D Z, HAN F, DING J J, et al. Microstructure and performance of brazed diamonds with multilayer graphene-modified Cu-Sn-Ti solder alloys [J]. Ceramics International,2021,47(16):22854-22863. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.04.304 [17] 张克从, 张乐潓. 晶体生长科学与技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1981.ZHANG Kecong, ZHANG Lehui. Crystal growth science and technology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1981. [18] 胡汉起. 金属凝固原理[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2000.HU Hanqi. Metal solidification principle[M]. Beijing: Mechanical Industry Press, 2000. [19] NAKA M, SCHUSTER J C , NAKADE I, et al. Determination of the liquidus of the ternary system Cu-Sn-Ti[J]. Journal of Phase Equilibria, 2001, 22(3): 352-356. [20] WANG J, LIU C L, LEINENBACH C. Experimental investigation and thermodynamic assessment of the Cu-Sn-Ti ternary system [J]. CALPHAD: Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry,2011,35:82-94. doi: 10.1016/j.calphad.2010.12.006 [21] 陈念贻. 键参数函数及其应用(一)金属键的形成条件 [J]. 中国科学,1974(6):580-584. [22] CHEN N Y. Bond parameter functions and their applications (一)—the formation conditions of metal bonds [J]. Science China,1974(6):580-584. [23] 孙茂才. 金属力学性能[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业出版社, 2005.SUN Maocai. Mechanical properties of metals [M]. Harbin: Harbin Industrial Press, 2005. -



 下载:
下载:



 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
