Application of diamond based materials and surface microchannel fabricationtechnology in efficient heat dissipation
-
摘要: 随着第三代半导体材料的兴起,电子器件逐渐向着高功率、小型化、集成化方向发展。传统散热技术已难以满足第三代半导体器件高热流的散热要求,由此带来的温度堆积问题成为器件失效的主要原因。金刚石基材料具有优异的散热性能,基于此材料的高效散热技术有望解决高热流散热难题。总结了金刚石基材料的发展及其表面微通道制备的主要方法,综述了金刚石基材料在高效散热领域中的应用和未来的发展方向。金刚石基材料高效散热技术的发展及应用能够为高热流密度散热难题的解决提供技术支撑。Abstract: With the rise of third-generation semiconductors, electronic devices are evolving towards high-power, miniaturization, and integration. Traditional heat dissipation technologies are no longer sufficient to meet the heat dissipation requirements of high heat flux in third-generation semiconductor devices. Temperature accumulation has become a major cause of device failure. Diamond-based materials have excellent thermal properties. Efficient heat dissipation technology based on these materials has become a key direction to solve the high heat flux dissipation problem. This article summarizes the development of diamond-based materials and the main methods for preparing surface microchannels. It reviews the application and development trends of diamond-based materials in the field of efficient heat dissipation. The development and application of diamond-based materials for efficient heat dissipation technology can provide technical support for addressing the problem of high heat flux dissipation.
-
Key words:
- diamond /
- microchannel /
- fabrication /
- efficient heat dissipation
-
图 2 紫外纳秒激光加工的金刚石微通道表面与截面形貌[25]
Figure 2. Surface and cross section morphology of diamond microchannel fabricated by ultraviolet nanosecond laser processing
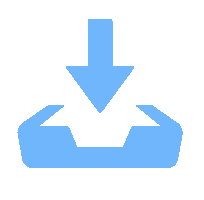
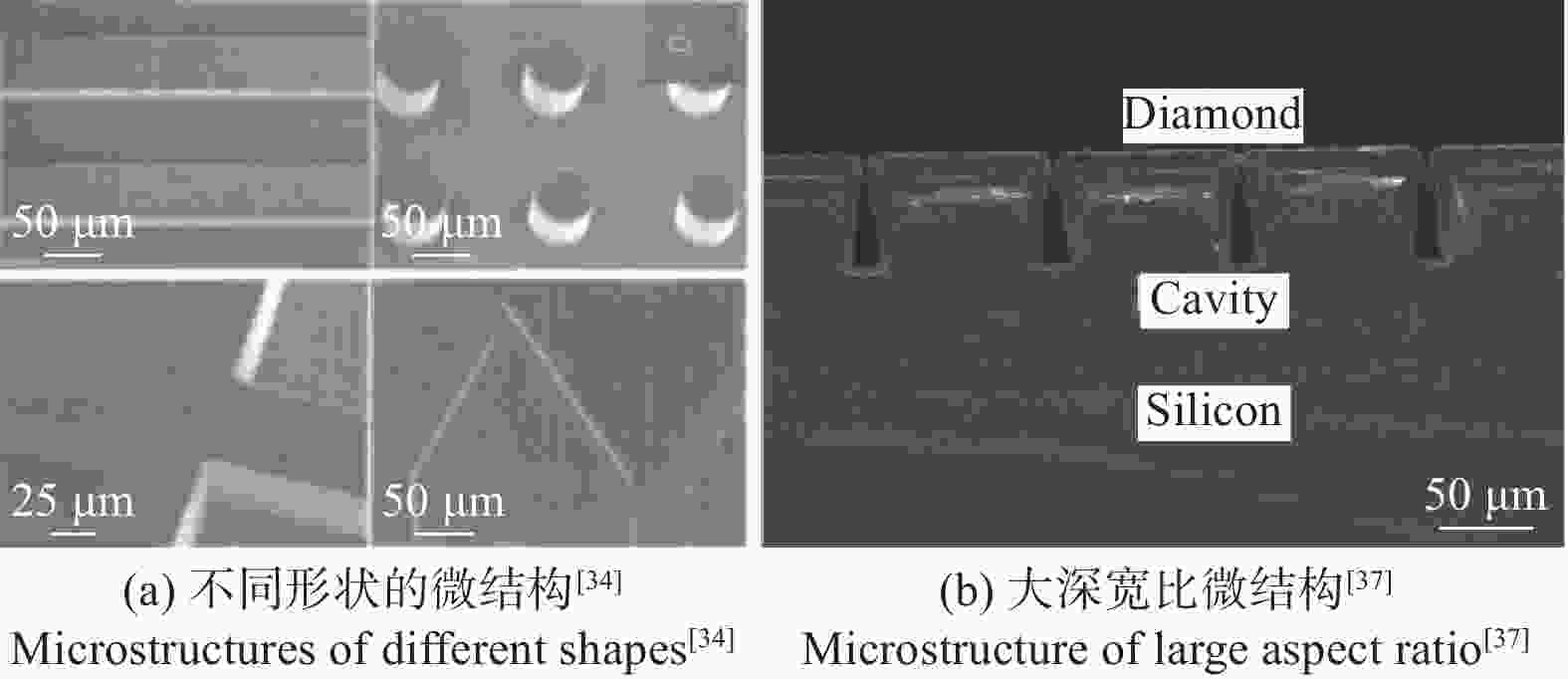
图 4 具有大深宽比的金刚石光学器件SEM图[29]
Figure 4. SEM image of diamond gratings with large aspect ratio
图 6 铜模板内沉积的三维金刚石膜[36]
Figure 6. 3D diamond film deposited on copper template
图 9 金刚石微通道的转变机理示意[39]
Figure 9. Schematic diagram of the change mechanism of diamond microchannel
材料 热膨胀系数/
(10−6·K−1)热导率/
(W·m−1·K−1)密度/
(g·cm−3)热导率/密度
(λ/ρ)Al 23.0 230 2.7 85.2 Cu 17.0 400 8.9 44.9 Mo 5.0 140 10.2 13.7 Kovar 5.9 17 8.3 2.0 Invar 1.6 10 8.1 1.2 Diamond 1.0~1.7 800~2 200 3.5 227.3~625.0 Diamond/Al 7.0~9.0 1 021 3.0 340.3 Diamond/Cu 4.0~7.0 900 5.0~6.0 150.0~180.0 表 2 金刚石材料微通道的研究情况
Table 2. Recent research on the diamond microchannels
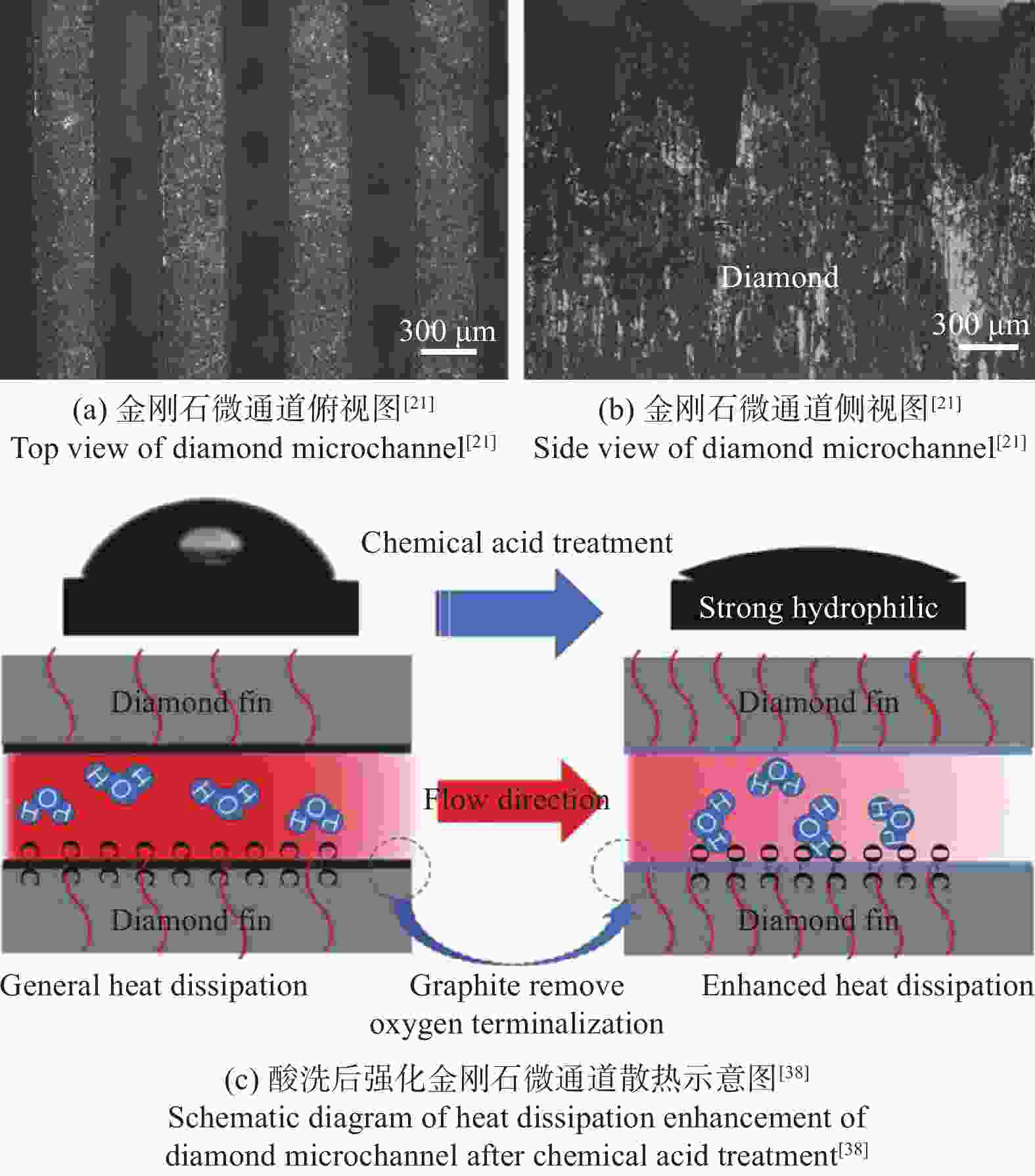
材料 散热能力 结论 文献来源 多晶金刚石 1 280 W/cm2热流 金刚石微通道高效散热并有效提高热源温度均匀性 [23] 多晶金刚石 267 W/cm2热流 金刚石能有效扩散热源中心热量 [19] 金刚石 600 W/cm2热流 占空比是影响金刚石微通道传热性能的主要因素 [40] 多晶金刚石 ≥1 kW/cm2热流 金刚石微通道在不同热流密度下,存在一个最佳入口质量流量 [22] 多晶金刚石 5 637.10~11 447.20 W/(m2·K)传热系数 金刚石微通道的传热系数较同条件下铝质微通道的提高37%~73% [21] 多晶金刚石 11 917 W/(m2·K)传热系数 亲水性金刚石微通道传热性能提升20%~50% [38] 硅 + 金刚石 热点区域1 600 W/cm2热流 热点区域温度均匀性提升41.7% [20] 表 3 针对金刚石热扩散层与微通道液冷散热相结合的研究情况
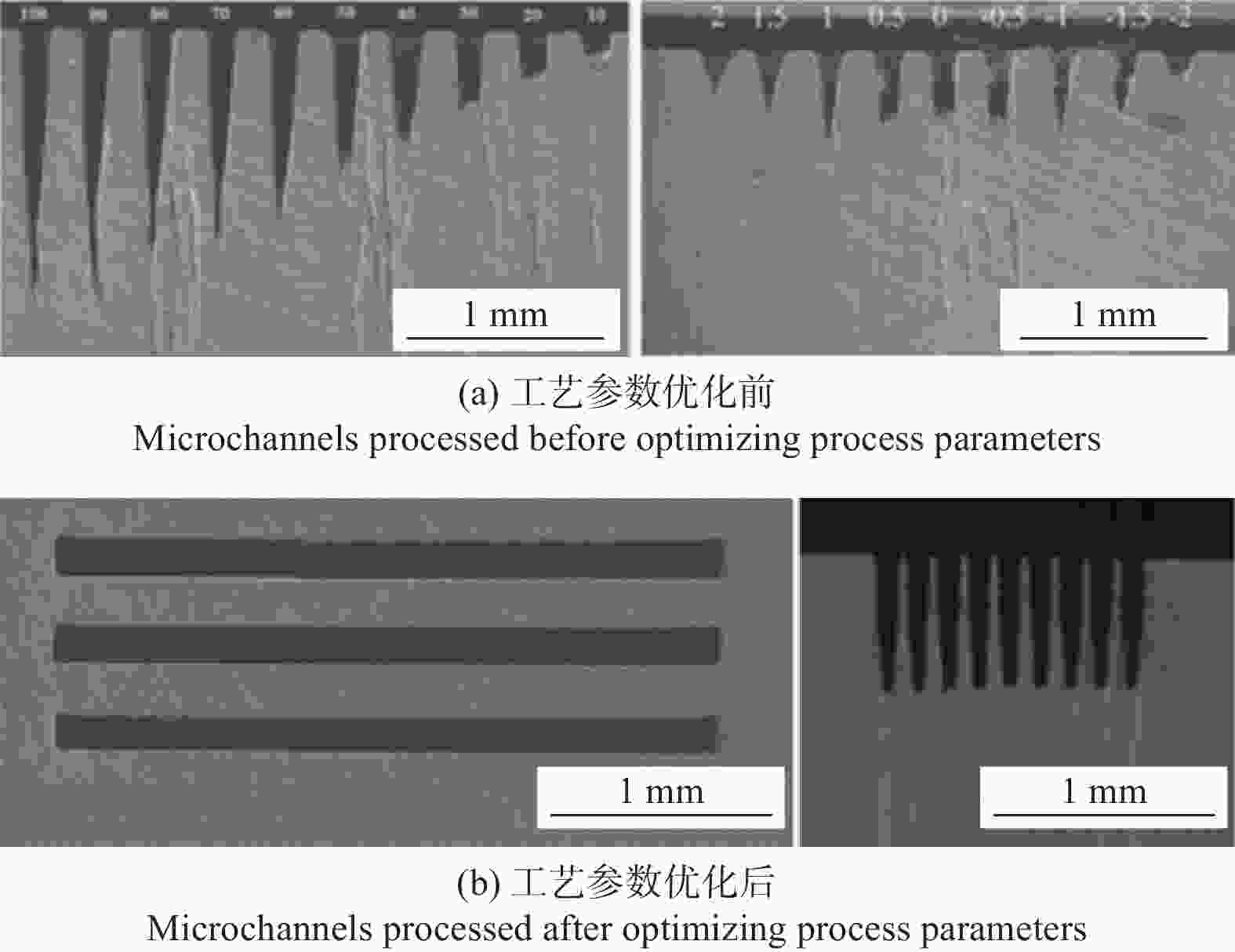
Table 3. Recent research on the combination of diamond heat spreader and microchannel liquid cooling
-
[1] NAQIUDDIN N H, SAW L H, MING C Y, et al. Overview of micro-channel design for high heat flux application [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2018(82):901-914. [2] BRINDA R, DANIEL R J, SUMANGALA K. Ladder shape micro channels employed high performance micro cooling system for ULSI [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2012,55(13/14):3400-3411. [3] 赵继文, 朱嘉琦, 郝晓斌, 等. 微波等离子体化学气相沉积法合成高导热金刚石材料及器件应用进展 [J]. 硅酸盐学报,2022,50(7):1852-1864.ZHAO Jiwen, ZHU Jiaqi, HAO Xiaobin, et al. Recent development on high thermal conductivity diamond synthesized by microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition and its devices applications [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2022,50(7):1852-1864. [4] 万晓昌, 刘欣蔚, 翟少华, 等. 高温高压合成大单晶金刚石晶体形态特征研究 [J]. 超硬材料工程,2020,32(4):8-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1433.2020.04.002WAN Xiaochang, LIU Xinwei, ZHAI Shaohua, et al. Study on crystal morphology of large single crystal diamond synthesized at high temperature and high pressure [J]. Superhard Material Engineering,2020,32(4):8-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1433.2020.04.002 [5] 毛梦嫒, 杨志军. 高温高压合成金刚石的机理、工艺及特征研究 [J]. 超硬材料工程,2021,33(5):15-24.MAO Mengyuan, YANG Zhijun. Mechanism, technology and characteristics of diamond synthesis under high temperature and high pressure [J]. Superhard Material Engineering,2021,33(5):15-24. [6] 蔡正浩. Fe-Ni-C-N-H-O体系高温高压合成金刚石的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023.CAI Zhenghao. Study on the synthesis of diamond in a Fe-Ni-C-N-H-O system at high pressure and high temperature [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023. [7] 游志恒. DC-CVD法制备大面积超纳米金刚石膜[D]. 武汉: 武汉工程大学, 2016.YOU Zhiheng. Large area ultrananocrystalline diamond films deposited by direct current chemical vapor deposition [D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Institute of Technology, 2016. [8] TABAKOYA T, KANADA S, WAKUI Y, et al. High-rate growth of single-crystalline diamond (100) films by hot-filament chemical vapor deposition with tantalum filaments at 3000℃ [J]. Physica Status Solidi(a),2019,216(21):1900244. doi: 10.1002/pssa.201900244 [9] LI Y F, SU J J, LIU Y Q, et al. Design of a new TM021 mode cavity type MPCVD reactor for diamond film deposition [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2014(44):88-94. [10] 吕反修. 我国直流电弧等离子体喷射金刚石膜制备技术历史、现状与趋势 [J]. 超硬材料工程,2014,26(2):18-25.LV Fanxiu. The history, current status and trend of the DC arc plasma jet diamond film preparation technique in China [J]. Superhard Material Engineering,2014,26(2):18-25. [11] 李义锋, 姜龙, 安晓明, 等. 化学气相沉积大尺寸多晶金刚石膜及其应用研究进展 [J]. 真空电子技术,2022(5):1-12,19.LI Yifeng, JIANG Long, AN Xiaoming, et al. A review on preparation and application of large area polycrystalline diamond films bt chemical vapor deposition [J]. Vacuum Electronics,2022(5):1-12,19. [12] HUANG Y, CHEN L, SHAO S, et al. The 7-in. freestanding diamond thermal conductive film fabricated by DC arc plasma jet CVD with multi-stage magnetic fields [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2022(122):108812. [13] EKIMOV E A, SUETIN N V, POPOVICH A F, et al. Thermal conductivity of diamond composites sintered under high pressures [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2008,17(4/5):838-843. [14] LI N, ZHANG Y J, ZHANG Y, et al. Realizing ultrahigh thermal conductivity in bimodal-diamond/Al composites via interface engineering [J]. Materials Today Physics,2022(28):100901. [15] 张荻, 谭占秋, 熊定邦, 等. 热管理用金属基复合材料的应用现状及发展趋势[J]. 中国材料进展, 2018, 37(12): 994-1001, 1047.ZHANG Di, TAN Zhanqiu, XIONG Dingbang, et al. Application and prospect of metal matrix composites for thermal management: an overview [J]. Materials China, 2018, 37(12): 994-1001, 1047. [16] ZWEBEN C. Advanced composites and other advanced materials for electronic packaging thermal management: International symposium on advanced packaging materials: processes, Properties & interfaces [C]//Braselton: IEEE, 2001: 360-365. [17] 高文迦, 贾成厂, 褚克, 等. 金刚石/金属基复合新型热管理材料的研究与进展 [J]. 材料导报,2011,25(3):17-22,26.GAO Wenjia, JIA Chengchang, CHU Ke, et al. Research and advances of diamond/metal composites for thermal management materials [J]. Materials Reports,2011,25(3):17-22,26. [18] 李苏, 张占辉, 韩善果, 等. 激光技术在材料加工领域的应用与发展 [J]. 精密成形工程,2020,12(4):76-85.LI Su, ZHANG Zhanhui, HAN Shanguo, et al. Application and development of laser technology in the field of material processing [J]. Journal of Netshape Forming Engineering,2020,12(4):76-85. [19] YANG Q, ZHAO J Q, HUANG Y P, et al. A diamond made microchannel heat sink for high-density heat flux dissipation [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering,2019(158):113804. [20] ANSARI D, JEONG J H. A silicon-diamond microchannel heat sink for die-level hotspot thermal management [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering,2021(194):117131. [21] QI Z, ZHENG Y, ZHU X, et al. An ultra-thick all-diamond microchannel heat sink for single-phase heat transmission efficiency enhancement [J]. Vacuum,2020(177):109377. [22] YANG Q, MIAO J, ZHAO J, et al. Flow boiling of ammonia in a diamond-made microchannel heat sink for high heat flux hotspots [J]. Journal of Thermal Science,2020(29):1333-1344. [23] PALKO J W, LEE H, ZHANG C, et al. Extreme two-phase cooling from laser-etched diamond and conformal, template-fabricated microporous copper [J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2017,27(45):1703265. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201703265 [24] 姜海涛, 崔健磊, 殷东平, 等. 雷达功率组件的金刚石微通道热沉激光加工工艺 [J]. 中国机械工程,2021,32(3):261-268.JIANG Haitao, CUI Jianlei, YIN Dongping, et al. Femtosecond laser processing technology of diamond micro-channel heat sink based on radar power module [J]. China Mechanical Engineering,2021,32(3):261-268. [25] 韦新宇, 温秋玲, 陆静, 等. 紫外纳秒激光加工金刚石微槽工艺参数优化研究 [J]. 中国激光,2022,49(10):96-106.WEI Xinyu, WEN Qiuling, LU Jing, et al. Research on parameters optimization of diamond microgrooves processed by ultravilot nanosecond laser [J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers,2022,49(10):96-106. [26] FU J, WANG Y, WANG J, et al. Fabrication of hundreds of microns three-dimensional single crystal diamond channel along with high aspect ratio by two-step process [J]. Materials Letters,2019(255):126556. [27] WEI Q, ZHANG X, LIN F, et al. Fabrication of micron scale three-dimensional single crystal diamond channel: by micro-jet water-assist laser [J]. Materials,2021(14):3006. [28] ZHOU J, XU R, JIAO H, et al. Study on the mechanism of ultrasonic-assisted water confined laser micromachining of silicon [J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering,2020(132):106118. [29] FORSBERG P, KARLSSON M. High aspect ratio optical gratings in diamond [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2013(34):19-24. [30] FU Y, DU H, MIAO J. Patterning of diamond microstructures on Si substrate by bulk and surface micromachining [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2003,132(1/2/3):73-81. [31] SUN P, TANG C, XIA X, et al. Controlled fabrication of periodically high-aspect ratio CVD-diamond nanopillar arrays by pure oxygen etching process [J]. Microelectronic Engineering,2016(155):61-66. [32] HICKS M L, PAKPOUR A C, JACK R B. Diamond etching beyond 10 μm with near-zero micromasking [J]. Scientific Reports,2019,9(1):15619. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51970-8 [33] ZHU T F, JIAO F, FANG L, et al. Fabrication of diamond microlens arrays for monolithic imaging homogenizer [J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2017(80):54-58. [34] 袁佳晶, 卢文壮, 王红军, 等. 基于模型复制法的金刚石微结构制备研究 [J]. 人工晶体学报,2010,39(5):1141-1145.YUAN Jiajing, LU Wenzhuang, WANG Hongjun, et al. Study on fabrication of diamond microstructure based on model replication technique [J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals,2010,39(5):1141-1145. [35] CHANDRAN M, ELFIMCHEV S, MICHAELSON S, et al. Fabrication of microchannels in polycrystalline diamond using pre-fabricated Si substrates [J]. Journal of Applied Physics,2017,122(14):145303. doi: 10.1063/1.5006608 [36] LIU X Z, ZHANG X W, YU Z M. Growth behavior of CVD diamond in microchannels of Cu template [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2015,25(6):2009-2017. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63810-9 [37] LU W Z, ZHU Y S, YUAN J J, et al. Limiting aspect ratio of diamond microstructure fabricated by model copy technology [J]. Integrated Ferroelectrics,2012,137(1):156-164. doi: 10.1080/10584587.2012.687328 [38] QI Z, ZHENG Y, WEI J, et al. Surface treatment of an applied novel all-diamond microchannel heat sink for heat transfer performance enhancement [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering,2020(177):115489. [39] TU J, SHI J, CHEN L, et al. Surface termination of the diamond microchannel and single-phase heat transfer performance [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2022(199):123481. [40] LI W, ZHU L, JI F, et al. Multi-parameters optimization for diamond microchannel heat sink[C]//2019 20th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology, 2019: 1-4. [41] 巫永鹏. 铜基金刚石复合材料的电镀法制备及热性能研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2020.WU Yongpeng. Cu-diamond composites prepared via electrodeposition and its thermal properties [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2020. [42] 张永建, 刘皓妍, 白光珠, 等. 铜-硼/金刚石复合材料翅片热沉散热研究 [J]. 半导体技术,2021,46(7):553-557,571.ZHANG Yongjian, LIU Haoyan, BAI Guangzhu, et al. Research on heat dissipation of Cu-B/diamond composite fin heat sink [J]. Semiconductor Technology,2021,46(7):553-557,571. [43] CONSTANTIN L, FAN L, PONTOREAU M, et al. Additive manufacturing of copper/diamond composites for thermal management applications [J]. Manufacturing Letters,2020(24):61-66. [44] ZHANG H, GUO Z, LU Y. Enhancement of hot spot cooling by capped diamond layer deposition for multifinger AlGaN/GaN HEMTs [J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices,2019,67(1):47-52. [45] ZHANG H, GUO Z. Thickness dependence and anisotropy of capped diamond thermal conductivity on cooling of pulse-operated GaN HEMTs [J]. IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging, and Manufacturing Technology,2021,11(2):233-240. doi: 10.1109/TCPMT.2021.3050976 [46] ZHANG H, GUO Z. Near-junction microfluidic cooling for GaN HEMT with capped diamond heat spreader [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2022(186):122476. [47] HAN Y, LAU B L, ZHANG X, et al. Enhancement of hotspot cooling with diamond heat spreader on Cu microchannel heat sink for GaN-on-Si device [J]. IEEE Transactions on Components Packaging & Manufacturing Technology,2014,4(6):983-990. [48] HAN Y, LAU B L, TANG G, et al. Thermal management of hotspots using diamond heat spreader on Si microcooler for GaN devices [J]. IEEE Transactions on Components Packaging & Manufacturing Technology,2015,5(12):1740-1746. [49] CALAME J P, MYERS R E, BINARI S C, et al. Experimental investigation of microchannel coolers for the high heat flux thermal management of GaN-on-SiC semiconductor devices [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2007,50(23/24):4767-4779. [50] CAMPBELL G, EPPICH H, LANG K, et al. Advanced cooling designs for GaN-on-diamond MMICs: International electronic packaging technical conference and exhibition [C]// San Francisco: American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2015. -



 下载:
下载:








 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS
